Table of contents
- Introduction
- Who Are AI Testers?
- Who Are Human Testers?
- How AI Testers Work in Real Projects
- How Human Testers Work in Real Projects
- AI Testers vs Human Testers: Comparison
- Real-World Use Cases: Where Human Testers Win
- Limitations of Human Testers
- The Reality: AI + Human Testers Working Together
- Skills Human Testers Must Learn to Stay Relevant
- Conclusion
AI Testers vs Human Testers: Why the Future of QA Needs Both
Introduction
Software is commonplace in our lives today through mobile applications, websites, games, banking systems, and educational platforms. The software we use every day impacts our lives in many ways. If it’s not functioning correctly, it’s going to have a negative effect on us sooner than later. This is where software testing comes in.
There’s been a lot of debate recently about whether AI testers and robots can take the place of human testers. Many believe that all testing in the future will be done by machines and artificial intelligence. Others believe that human testers will continue to play a significant role and will always be required. People who have been through Quality Assurance Training for testers know that there is more to testing than clicking buttons on computers – you need to think critically about how to test from an end-user point of view and know what questions to ask.
Let’s take a look at both AI Testers and Human Testers and what they do in relation to delivering projects in real-time.
Who Are AI Testers?

What AI Testers Are
AI testers are neither robots nor humans, rather they’re software applications that utilize Artificial Intelligence (AI) technology to perform various aspects of software testing. The AI testers themselves do not have human-like thought processes, but these types of tools are able to learn from the history of previous testing activities and application actions to speed up and enhance the effectiveness of the software testing process.
What Types of Software Testing Tools Use AI?
Some AI tools for software testing have the abilities to:
- Build test cases automatically.
- Identify changes in the User Interface (UI) and update corresponding test scripts accordingly.
- Evaluate the test results and any ETL Logs.
What Applications Can Be Performed with AI?
Currently AI tools for software testing allow:
- To create test cases based upon previously collected data.
- Run very quickly.
- Identify patterns in failures.
- Eliminate unnecessary repetitive manual labor.
In short, AI does a good job providing rapid & reliable handling of boring and redundant tasks thereby allowing people to devote their attention to testing that is more creative and time-consuming.
Who Are Human Testers?

Humans who test software do more than just look for bugs. They also do several types of tests including:
- Manual Testing is when the tester simulates what a normal user would do when using the application (for example, clicking buttons and filling out forms) to see if the application works as it should and meets the expectations of the users.
- Automated Testing is when a test is created via scripts for repetitive tasks and/or larger applications which were done using Manual Testing.
- Analyzing Requirements: The tester also compares the software with the requirement to determine if the software supports the user or business needs.
- Anticipating Issues: Before testing, the tester considers potential problems, such as What happens if…? What would cause confusion to the user? etc. For example, in using a new social media application, a tester will post a photo in ways not intended by the developer to ensure that nothing breaks in the process.
While AI cannot replicate all human capabilities, it does offer humans additional benefits. Consider the following:
- Human testers can create hypothetical test cases, such as “What would happen if a customer clicked the ‘Submit’ button twice?”
- Human testers can see that certain designs make it difficult for people to navigate the system or are otherwise not friendly to users.
- Human testers have an inherent sense of when something is off, even if no error messages appear.
For example, a human tester could identify that a checkout button is being blocked by a large graphic on a shopping website — something an AI tester would probably overlook.
When it comes to testing teams, human testers do not operate in a vacuum but rather communicate with:
- Developers to discuss why bugs are significant and what steps they should take to resolve them;
- Designers to solicit input regarding usability and user experience of the product;
- Product owners to define the expectations and priorities associated with the creation of the product.
Human testers also help the software development team have a better understanding of the quality of their product beyond simply detecting bugs. Testers serve as an intermediary between the technical aspects of developing software and using the software in a real-world environment.
How AI Testers Work in Real Projects
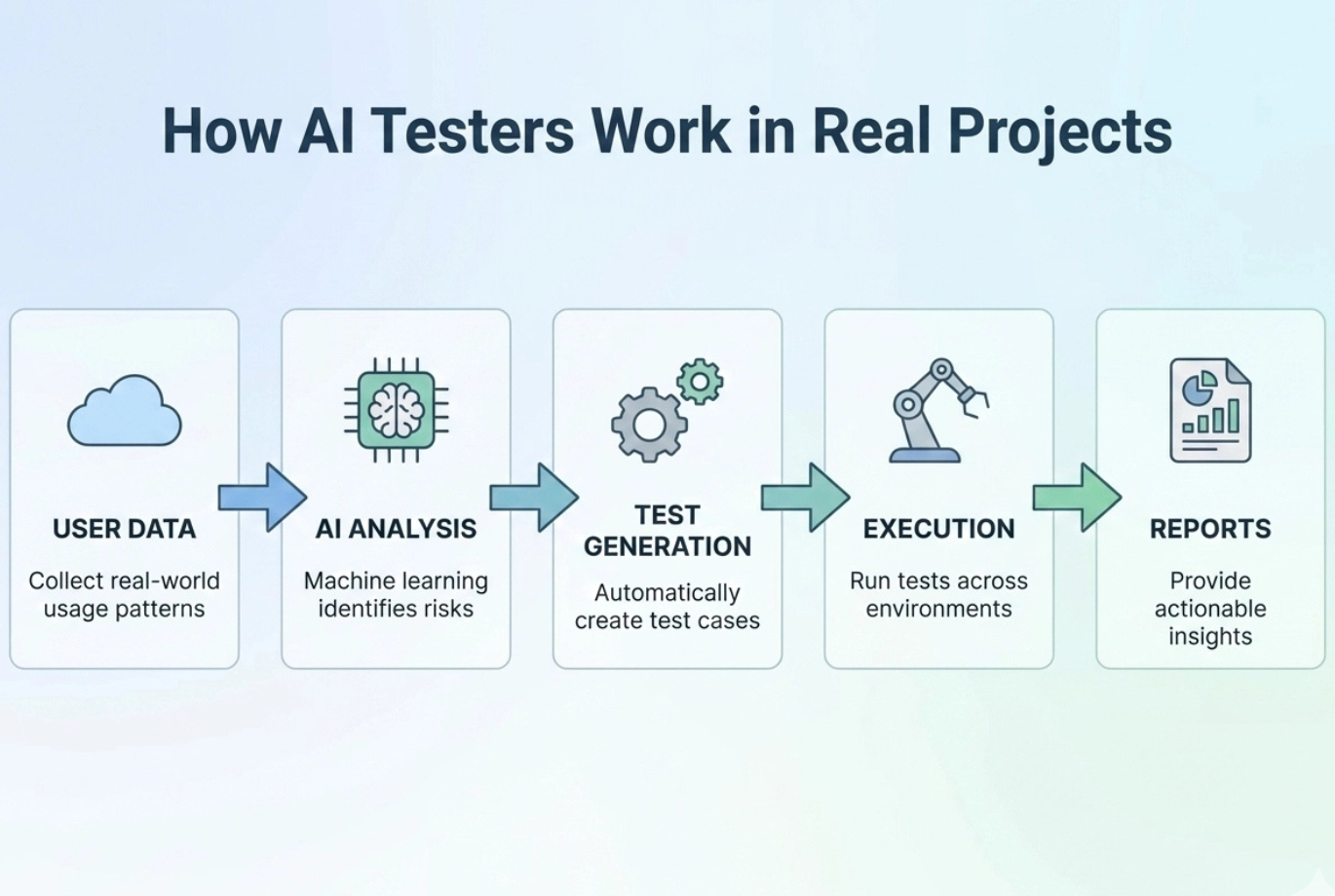
Generating Test Cases with AI
AI has the ability to analyse data to automatically create test cases based on user behaviour, logs, and historical testing data.
For example, if a lot of users are experiencing difficulty when trying to login to your site, AI will generate all possible test cases to cover this event.
Maintaining Automated Scripts
AI can automatically update automated scripts to reflect small changes to software (e.g. renaming of buttons). The AI saves time and effort by making sure that automated tests remain functional.
Testing, Analysis, and Reporting with AI
AI can quickly execute test cases in bulk, identify patterns from analysis of failure reports, and present data in a simple and clear report. For instance, AI can group errors based on their associated module, enabling faster resolution of these issues by developers.
Where AI is Beneficial
AI is great for repetitive and tiresome activities such as:
* Performing regression testing after an upgrade
* Performing tests repeatedly across multiple versions
* Large applications with thousands of associated test cases
Overall, AI testers provide a faster alternative to traditional testers as they require less manual time and can free up human testers to perform higher-level intellectual and creative tasks.
How Human Testers Work in Real Projects
The process of assessing Business Requirements
Human testers understand the context of features and what those features mean to users and businesses.
Example: A ‘favorites’ button allows the user to quickly re-order items and meets a need of the shopper.
Exploratory testing as well as Usability Testing.
Human testers test for the user when there is no formalised scripted approach to testing. They simulate actual user’s behaviour (real time) and catch possible issues that an AI might miss.
Example: Adding or removing products to/from a shopping cart, logging out then checking to see if the cart saved what you added.
Edge Cases & Unexpected Scenarios.
Developers and Stakeholders - How Testers Communicate to them.
Testers provide their understanding of the definition of a “bug” and how they think the presence of bugs affect the end-user. This information helps the development and stakeholder groups make decisions on how to prioritize and where to direct their correction efforts.
One Example: Customers get frustrated when payments take too long, resulting in fewer purchases.
AI Testers vs Human Testers: Comparison

AI and human testers each have distinct advantages and disadvantages. An overview of the differences follows below:
| Aspect | AI Testers | Human Testers |
| Speed | AI is capable of running thousands of tests in a matter of minutes—considerably quicker than a human can. | Humans take longer to run tests manually and to analyze the results. |
| Scalability | AI has no problem scaling up to larger applications and processing huge amounts of data. | Human efforts are limited by the amount of time and energy they have, making scaling their efforts a much more complex task than scaling an AI. |
| Accuracy | AI consistently performs repetitive jobs and hardly makes mistakes. | Humans perform inconsistently, humans will create mistakes when fatigued or distracted. |
| Cost | AI tools require high setup and licensing costs initially. | Humans have ongoing salary and training costs. |
| Understanding users | AI has little understanding of user behavior or needs. | A human can have empathy with users and conduct usability and experience tests. |
| Creative Thinking | AI cannot think creatively or envision unique possibilities. | humans possess a creative mind that is able to create random occurrences and develop new uses. |
Real-World Use Cases: Where Human Testers Win
In general, human testers excel in creativity, judgment, and empathizing with their users. Below are examples of ways that human testers excel:
- Exploratory testing: Exploratory testing allows the tester (the human being) to “free-range” the software, as well as attempt unexpected actions on the software, to help discover issues (or defects) that may not have been found previously.
- UI and Usability Testing: Both UX and Usability Testing assess how easy it is to use, understand, and navigate through a software/application, as well as the level of frustration experienced by users of the software/application.
- Accessibility Testing: They ensure that a software application will function with users who have disabilities.
- Early Product Testing: Human testers evaluate a product’s compliance with ambiguous or changing requirements while providing important feedback.
- Interacting with Vagueness: They interpret ambiguous instructions, and through experience and intuition, they use both to produce relevant results.
In essence: Human testers demonstrate extraordinary aptitude for conducting most tasks that call for thinking, empathy, and creativity. They find problems that AI may not detect, and they verify how well a product will function for an actual user.
Limitations of Human Testers
While human testers excel in creativity, intuition, and experience, there are certain limitations inherent to the human experience which prevents them from achieving many of the results provided by artificial intelligence (AI). Human testers may:
- Get tired: Humans cannot work indefinitely, and extended test sessions impair focus and increase the incidence of error.
- Make errors: Even experienced testers may not detect all possible defects because of error pathways that occur with repetitive and/or complicated testing efforts.
- Take longer for extensive projects: Manual test execution of hundreds or thousands of features requires more time than AI-based execution.
- Repetitive Tasks: Many times, testers get bored doing repetitive tasks such as running several hundred of the same tests or making tiny adjustment to checks that take a very long time, which in most cases, causes decreased efficiency.
To sum it up, testers are better at using their minds to think, explore, and understand software than artificial intelligence is at being fast, scalable, and consistent.
The Reality: AI + Human Testers Working Together

The future of software testing will not see “AI versus Humans,” rather, the future will exist with both AI and Humans collaborating as partners. There are some notable differences between AI and human contributions to software testing, namely speed/consistency with AI vs creativity/intuitiveness/understanding of users by humans.
Human in the Loop Testing
A popular method of human in the loop testing involves AI and human testers working together.
- AI conducts large scale and/or repetitive testing as well as data-driven testing very quickly and accurately;
- Human Testers review AI generated test results by identifying and prioritizing defects, verifying artificial test results to ensure they are not a result of false positives;
- Human Testers develop the plan of action for the defects identified by the AI generated test results, creating a prioritized list of defects and recommending enhancements based on their knowledge of the user’s experience.
Therefore, while AI takes care of heavy work load in software testing, human judgment remains at the forefront of identifying and prioritizing quality related decisions.
Modern QA teams balance speed and thoughtfulness:
• Speed is achieved through AI – running of lots of tests, automating repetitive activities, generating reports quickly.
• Thoughtfulness comes from humans – creatively exploring the software, understanding user needs, and making intelligent, high-level QA decisions.
Through this partnership, modern QA teams can quickly deliver high-quality software. AI reduces the amount of routine work that has to be performed by people, and people ensure that the software functions properly for actual users. The combination of these two approaches creates a testing process that is efficient and intelligent.
Skills Human Testers Must Learn to Stay Relevant
As AI takes a bigger part in software testing, the tester must learn new skills in order to remain relevant:
- Try using the basic types of tools, as well as how to use them. This knowledge helps testers use AI tools for testing instead of competing with them for doing the same thing.
- Basic automation skills: The ability to create and maintain automated scripts is still valuable for test engineers to use to expedite their work and allow them time for advanced testing, regardless of how much assistance you receive from artificial intelligence.
- Creating prompts for use with AI Tools: The majority of AI Tools operate based on instructions or prompts for task execution. The testers’ ability to write clear prompts will enable them to direct AI to produce accurate test cases or reports.
- The testers will need to expand their ability to analyze results. They need to understand user needs and how to apply their domain knowledge when interpreting AI output and deciding how to use that information in their testing process.
Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence is transforming the field of software testing, however Artificial Intelligence is an aid for software test engineers and not a substitute for their work – Human Software Testers are creative thinkers and understand the intent of the customer, a capacity which Artificial Intelligence does not yet possess.
The most successful Quality Assurance teams use an integrated approach of using artificial intelligence with Human Software Testers to develop the most comprehensive, secure and user-friendly software.
Ultimately software quality is not about what is created by machines or created by humans, rather it is about both working together so that software can be improved and provide maximum benefit to all.

