TestNG vs Cucumber: Key Insights for Making the Best Choice in Your Automation Framework
Introduction
With the constant increase in software systems, automation testing frameworks have been become essential in order to deliver quality, reliable and high applications. Two testing frameworks in the Java-based ecosystem that are popular are TestNG and Cucumber — both offer substantial capabilities, but both have different philosophies.
Deciding between TestNG and Cucumber comes down to several considerations: the goals of your project, how technically skilled is your team, and the level of collaboration between QA, Development and Business Stakeholders.
This blog, will go through a practical, thorough comparison of TestNG and Cucumber. It will provide you with their capabilities, advantages and disadvantages, in addition to their use cases; thereby allowing you to decide on the best automation testing tool to meet your demands.
If you are new to the automation testing world, or you want to further develop your knowledge, you can decide on a formal Software Testing Course, that will give you in-depth training on the frameworks and how they are best applied in reality.
What is TestNG?
Origin and Purpose
TestNG (Test Next Generation) is a great testing framework based on JUnit that was built to provide easier, scalable automated testing for Java applications. It was founded by Cedric Beust to provide more functionality and flexibility than existing unit test frameworks.
Core Features
- Annotations such as: @Test, @BeforeMethod, @AfterSuite
- XML suite configuration for higher level orchestration
- Group, priority and dependencies management
- Data-driven testing using @DataProvider
- Native support for parallel execution
- Strong integrations with Selenium, Maven, Jenkins and other reporting tools
Use Cases
- Unit testing of Java components
- Integration and API testing
- UI test automation using Selenium WebDriver
- Smoke, sanity, and regression testing pipelines
What is Cucumber?
Where It Came From and What It Does
Cucumber is an open source Testing Tool using Behavior Driven Development. It allows tests to be written in natural language. Cucumber helps developers, business analysts and testers work together by converting specifications into automated tests.
Core Concepts
- Use of Gherkin Language: structured plain-English syntax with keywords – Given, When, and Then
- Feature Files: files that contain business-readable test scenarios
- Step Definitions: Java methods that implement the behavior described in the Gherkin steps
- Glue Code: how the Gherkin steps are tied to underlying testing logic
Use Cases
- UI or end-to-end test automation
- Projects where specifications evolve through collaboration
- Agile teams practicing test-first or story-driven development
- Scenarios requiring living documentation or traceable user behaviour
Pros and Cons

TestNG
Pros:
- Mature and stable framework with higher level of test control
- Fast execution and parallelisation is easy
- Great for unit/API/back-end testing
- Clear structure and simple integration for CI/CD tools
Cons:
- Not as readable for non-technical stakeholders
- Not a BDD-style documentation, doesn’t consider user behavior.
Cucumber
Pros:
- Human-readable scenarios create collaboration across roles
- Encourages writing tests from the perspective of the user
- Encourages aligning to product requirements
- Allows BDD-style practices
Cons:
- Involves overhead of maintaining step definitions
- Involves more setup to run in parallel
- Unstructured feature files can cause duplication, and confusing.
Use Case Comparison
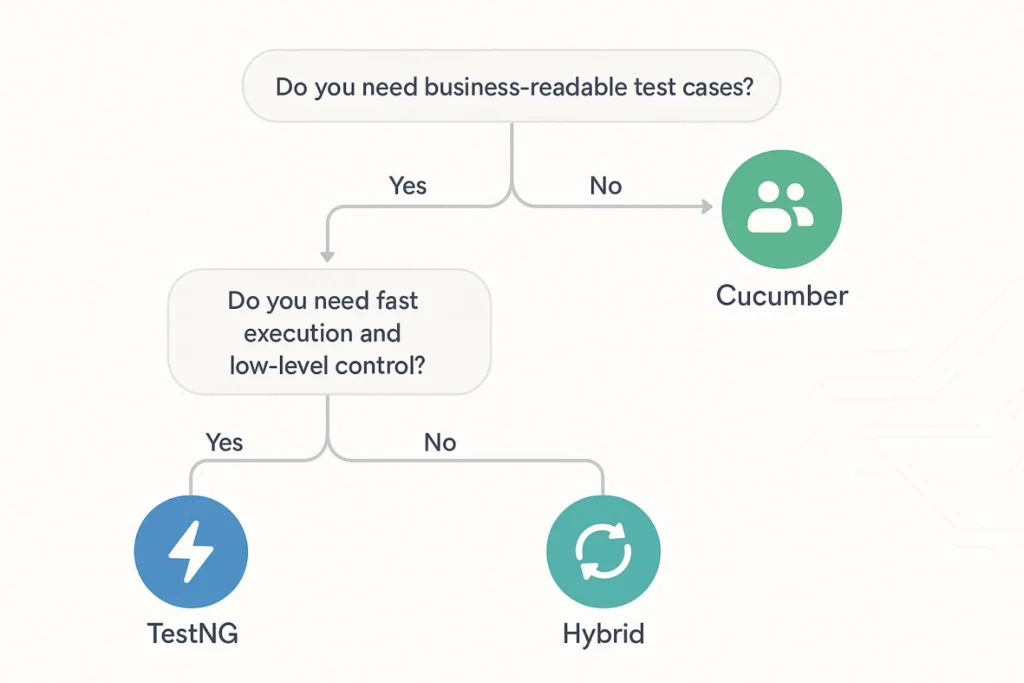
When to Use TestNG
- You need a fast, modular testing solution for Java applications
- Your team consists primarily of developers and QA engineers
- The test cases are low-level (unit, API, functional)
- You require fine-grained test execution control and configurations
When to Use Cucumber
- Your project demands collaboration between dev, QA, and product teams
- Test cases need to be written in a business-readable format
- You follow BDD practices or write acceptance criteria in Gherkin
- You want your tests to serve as documentation of system behaviour
Integration with Selenium
java
CopyEdit
public class LoginTest {
@BeforeMethod
public void setUp() {
// Initialize WebDriver
}
@Test
public void verifyLogin() {
// Login test logic
}
@AfterMethod
public void tearDown() {
// Quit browser
}
}
gherkin
CopyEdit
Feature: Login
Scenario: Successful login
Given the user is on the login page
When the user enters valid credentials
Then the user should be redirected to the homepage
java
CopyEdit
@Given(“the user is on the login page”)
public void openLoginPage() {
// Selenium code to open login page
Maintainability & Scalability
TestNG
TestNG offers strong maintainability through its use of modular test classes, centralized configuration files, and organized test suites. TestNG is very scalable, even for larger codebases, and it provides an interface for achieving clean UI automation architecture using the Page Object Model.
Cucumber
Team & Project Suitability
Understanding your team’s structure and project dynamics is critical when selecting a framework.
When TestNG Fits Best
- Teams comprised of technical testers and developers who prefer control and performance
- Projects with a strong focus on unit testing, integration testing, or API automation
- CI/CD-driven environments requiring high-speed execution and robust suite configuration
- Organizations with mature automation pipelines and less need for business stakeholder collaboration
When Cucumber is Ideal
- Cross-functional Agile teams where collaboration across roles is essential
- Projects emphasizing behavior validation and user flows
- Business-critical applications where acceptance criteria are detailed and traceable
- Organizations practicing BDD or where product owners need visibility into test scenarios
Hybrid Strategy: Best of Both Worlds
Many enterprise teams leverage both tools in a layered testing strategy:
- Use Cucumber to define high-level acceptance tests and UI journeys.
- Use TestNG for low-level functional, integration, and API testing.
This allows teams to balance technical efficiency with collaborative clarity.
Key Differences (Table Format)
| Feature | TestNG | Cucumber |
| Test Syntax | Java code with annotations (@Test, @BeforeMethod, etc.) | Gherkin language (Given, When, Then) + Java step definitions |
| Readability | Optimized for developers and technical testers | Highly readable by non-technical users (e.g., BAs, Product Owners) |
| Execution Model | Annotation-based execution using XML or Java class runners | Feature file-based execution mapped via step definitions |
| Parallel Execution | Built-in support with simple XML configuration | Requires integration with TestNG/JUnit and additional setup |
| Maintainability | High, with modular test class design and suite configuration | Medium, requires careful handling of step duplication and naming |
| Scalability | Easily scalable in large test suites | Scales with discipline; step management becomes challenging at scale |
| Collaboration | Limited to QA/Dev teams | Encourages collaboration across QA, Dev, BA, and Product |
| Learning Curve | Low to moderate for Java developers | Moderate for technical users; low for stakeholders reading Gherkin |
| Use Case Alignment | Unit, integration, and API tests | UI workflows, business logic validation, and end-to-end user scenarios |
| Tooling & Reporting | Supports Allure, ExtentReports, built-in TestNG reports | Requires plugins (e.g., Cucumber Reports, Allure) for detailed reporting |

Conclusion
Both TestNG and Cucumber are fantastic frameworks singled out for different purposes:
- TestNG is perfect for developers and technical testers focused on backend, unit, and API tests with full control over execution.
- Cucumber was built for collaboration. It helps streamline communication and understanding in an agile team by making tests readable and traceable across roles.
Your choice should be based on not just some technical capabilities, but also upon considering who is coding the tests, who needs to understand them, and how those tests are shaping your product’s quality.
For many real-world projects, a hybrid approach may be most beneficial — taking the clarity of Cucumber and merging it with the speed and robustness of TestNG.

